
Sample summary
sample_summary.RmdCreate Metaboprep object
library(metaboprep)
# import data
data <- read.csv(system.file("extdata", "dummy_data.csv", package = "metaboprep"), header=T, row.names = 1) |> as.matrix()
samples <- read.csv(system.file("extdata", "dummy_samples.csv", package = "metaboprep"), header=T, row.names = 1)
features <- read.csv(system.file("extdata", "dummy_features.csv", package = "metaboprep"), header=T, row.names = 1)
# create object
mydata <- Metaboprep(data = data, samples = samples, features = features)Summary of Metaboprep object
summary(mydata)
#> Metaboprep Object Summary
#> --------------------------
#> Samples : 100
#> Features : 20
#> Data Layers : 1
#> Layer Names : input
#>
#> Sample Summary Layers : none
#> Feature Summary Layers: none
#>
#> Sample Annotation (metadata):
#> Columns: 5
#> Names : sample_id, age, sex, pos, neg
#>
#> Feature Annotation (metadata):
#> Columns: 5
#> Names : feature_id, platform, pathway, derived_feature, xenobiotic_feature
#>
#> Exclusion Codes Summary:
#>
#> Sample Exclusions:
#> Exclusion | Count
#> -----------------
#> user_excluded | 0
#> extreme_sample_missingness | 0
#> user_defined_sample_missingness | 0
#> user_defined_sample_totalpeakarea | 0
#> user_defined_sample_pca_outlier | 0
#>
#> Feature Exclusions:
#> Exclusion | Count
#> -----------------
#> user_excluded | 0
#> extreme_feature_missingness | 0
#> user_defined_feature_missingness | 0Run sample summary
# note that for illustrative purposes we are using a log outlier unit distance of 1.0 here, in practice we tend to favor a value of 5.0.
sample_sum1 <- sample_summary(metaboprep = mydata,
source_layer = "input",
outlier_udist = 1.0,
output = "data.frame")Table of sample summary
| sample_id | missingness | tpa_total | tpa_complete_features | outlier_count |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id_100 | 0 | 38.699 | 38.699 | 0 |
| id_99 | 0 | 39.451 | 39.451 | 0 |
| id_98 | 0 | 45.135 | 45.135 | 1 |
| id_97 | 0 | 37.289 | 37.289 | 2 |
| id_96 | 0 | 31.545 | 31.545 | 3 |
| id_95 | 0 | 36.751 | 36.751 | 2 |
| id_94 | 0 | 37.384 | 37.384 | 0 |
| id_93 | 0 | 34.069 | 34.069 | 0 |
| id_92 | 0 | 38.942 | 38.942 | 0 |
| id_91 | 0 | 42.743 | 42.743 | 2 |
Run sample summary on subset
Using the sample_ids and feature_ids
arguments you can run the summary for a subset of the data. Note: all
rows will be return, however summary data will only be returned for the
specified ids.
## define a vector of sample IDs
sids <- mydata@samples[mydata@samples$sex == "female", "sample_id"]
## define a vector of feature IDs
fids <- mydata@features[, "feature_id"] |> sample(10)
# run sample summary on subset
sample_sum_subset <- sample_summary(metaboprep = mydata,
source_layer = "input",
outlier_udist = 1.0,
sample_ids = sids,
feature_ids = fids,
output = "data.frame")Table of sample summary on subset
| sample_id | missingness | tpa_total | tpa_complete_features | outlier_count |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id_98 | 0 | 22.241 | 22.241 | 0 |
| id_97 | 0 | 15.765 | 15.765 | 1 |
| id_96 | 0 | 17.082 | 17.082 | 1 |
| id_94 | 0 | 17.010 | 17.010 | 0 |
| id_93 | 0 | 17.478 | 17.478 | 1 |
| id_92 | 0 | 22.147 | 22.147 | 0 |
| id_90 | 0 | 14.568 | 14.568 | 1 |
| id_89 | 0 | 22.601 | 22.601 | 1 |
| id_88 | 0 | 18.243 | 18.243 | 2 |
| id_87 | 0 | 17.149 | 17.149 | 0 |
Run PCA analysis
pc_and_outliers() performs principal component analysis.
Missing data is imputed to the median and used to identify the number of
informative or ‘significant’ PCs by (1) an acceleration analysis, and
(2) a parallel analysis. Finally the number of sample outliers are
determined at 3, 4, and 5 standard deviations from the mean on the top
PCs as determined by the acceleration factor analysis.
pc_analysis <- pc_and_outliers(metaboprep = mydata,
source_layer = "input",
sample_ids = sids, ## It is also possible to run on a subset of samples and/or features
feature_ids = NULL
)Table of PCA analysis results
Returned are the PC eigenvectors for the top 10 PCs, and outlier counts at 3, 4, and 5 standard deviations from the mean for the top two PCs
| sample_id | pc1 | pc2 | pc3 | pc4 | pc5 | pc6 | pc7 | pc8 | pc9 | pc10 | pc1_3_sd_outlier | pc2_3_sd_outlier | pc3_3_sd_outlier | pc1_4_sd_outlier | pc2_4_sd_outlier | pc3_4_sd_outlier | pc1_5_sd_outlier | pc2_5_sd_outlier | pc3_5_sd_outlier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id_98 | 1.504 | -0.899 | -0.072 | -0.987 | 1.221 | 0.429 | -1.603 | 0.586 | -1.086 | -0.193 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_97 | 0.826 | 0.458 | 1.623 | 0.188 | -1.195 | 1.666 | -1.318 | -2.481 | -1.081 | 1.007 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_96 | -2.067 | 0.785 | -1.024 | 1.720 | 1.435 | 0.663 | 1.057 | -0.073 | -1.554 | -0.479 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_94 | -1.635 | 1.103 | 0.791 | 1.214 | -0.920 | -0.986 | 1.635 | 0.401 | -0.521 | 1.214 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_93 | -1.399 | 1.202 | -0.168 | -2.277 | 1.068 | -1.482 | -0.129 | -1.497 | 0.834 | 1.243 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_92 | 2.299 | 0.640 | 1.312 | 0.308 | -0.094 | 0.492 | 0.595 | -0.751 | 0.994 | -1.484 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_90 | -0.723 | 1.214 | 1.251 | 1.834 | -1.257 | 0.548 | -1.184 | -1.282 | 0.829 | 0.076 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_89 | -0.292 | 0.097 | 2.914 | 1.079 | -0.734 | -1.654 | 0.601 | 0.015 | -0.721 | 0.914 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_88 | 2.664 | 1.542 | -2.028 | 0.080 | 0.419 | -0.416 | 1.305 | -1.710 | 0.352 | -0.213 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_87 | -2.053 | 0.898 | -0.883 | 0.960 | 0.578 | 1.764 | -0.703 | 0.158 | 0.812 | 0.708 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Additional attributes
In addition, the variance explained vector is appended to the
returned data.frame as and attribute. This can
be accessed with the attribute name: [source_layer]_varexp,
in this case we used the input data, therefore the
attribute name is input_varexp. In a similar way, the
results of the acceleration analysis (input_num_pcs_scree)
and a parallel analysis (input_num_pcs_parallel) can also
be extracted.
library(ggplot2)
# extract varexp from attributes
varexp <- attr(pc_analysis, 'input_varexp')
# subset to top 100 for nicer plotting
if (length(varexp) > 100) varexp <- varexp[1:100]
# get acceleration and parallel analysis results
af <- attr(pc_analysis, 'input_num_pcs_scree')
np <- attr(pc_analysis, 'input_num_pcs_parallel')
if (af==np) np <- np+0.1 # make line visible if equal
# as data.frame
x_labs <- sub("(?i)pc","", names(varexp))
ve <- data.frame("pc" = factor(x_labs, levels=x_labs),
"var_exp" = varexp)
lines <- data.frame("Analysis" = c("Acceleration", "Parallel"),
"pc" = c(af, np))
# plot
ggplot(ve, aes(x = pc, y = var_exp)) +
geom_line(color = "grey") +
geom_point(shape = 21, fill = "#377EB8", size = 2) +
geom_vline(data = lines, aes(xintercept = pc, color = Analysis), inherit.aes = FALSE) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("Acceleration"="#E41A1C", "Parallel"="#4DAF4A")) +
scale_x_discrete(labels = function(x) ifelse(seq_along(x) %% 10 == 0 | x==1, x, "")) +
labs(x = "PC", y = "Variance explained") +
theme_classic() +
theme(legend.position = "top")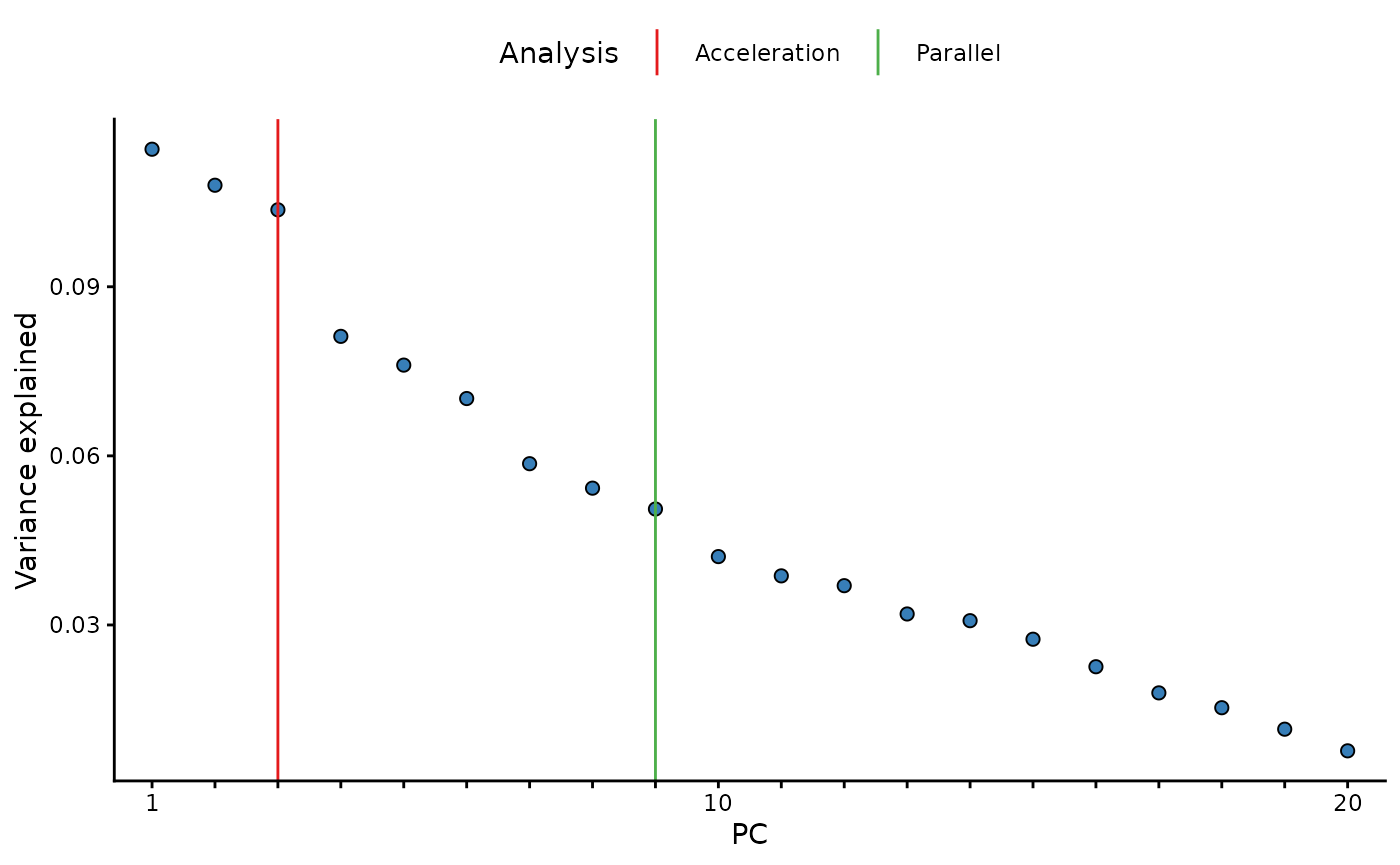
Run sample & feature summaries together
sf_sum <- summarise(metaboprep = mydata,
source_layer = "input",
outlier_udist = 1.0,
tree_cut_height = 0.5,
sample_ids = sids, ## It is also possible to run on a subset of samples and/or features
feature_ids = NULL,
output = "data.frame")
## two data frames are returned as a list object
names(sf_sum)
#> [1] "sample_summary" "feature_summary"Table of sample summary on subset
Note that when the summarise() function is used the sample summary now includes PCA derived summary data. This is not the case when the sample_summary() function is run alone, as seen above. The reason for the difference is because the PCA data is dependent upon the feature_summary() analysis.
Also, please note that when running on a subset, you are returned the
full summary for all samples and features, but only the summary data for
the specified subset will be populated, the rest will be
NA.
| sample_id | missingness | tpa_total | tpa_complete_features | outlier_count | pc1 | pc2 | pc3 | pc4 | pc5 | pc6 | pc7 | pc8 | pc9 | pc10 | pc1_3_sd_outlier | pc2_3_sd_outlier | pc3_3_sd_outlier | pc1_4_sd_outlier | pc2_4_sd_outlier | pc3_4_sd_outlier | pc1_5_sd_outlier | pc2_5_sd_outlier | pc3_5_sd_outlier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id_100 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| id_99 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| id_98 | 0 | 45.392 | 45.392 | 1 | 1.504 | -0.899 | -0.072 | -0.987 | 1.221 | 0.429 | -1.603 | 0.586 | -1.086 | -0.193 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_97 | 0 | 37.473 | 37.473 | 3 | 0.826 | 0.458 | 1.623 | 0.188 | -1.195 | 1.666 | -1.318 | -2.481 | -1.081 | 1.007 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_96 | 0 | 32.042 | 32.042 | 3 | -2.067 | 0.785 | -1.024 | 1.720 | 1.435 | 0.663 | 1.057 | -0.073 | -1.554 | -0.479 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_95 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| id_94 | 0 | 37.615 | 37.615 | 2 | -1.635 | 1.103 | 0.791 | 1.214 | -0.920 | -0.986 | 1.635 | 0.401 | -0.521 | 1.214 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_93 | 0 | 34.238 | 34.238 | 1 | -1.399 | 1.202 | -0.168 | -2.277 | 1.068 | -1.482 | -0.129 | -1.497 | 0.834 | 1.243 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_92 | 0 | 39.200 | 39.200 | 1 | 2.299 | 0.640 | 1.312 | 0.308 | -0.094 | 0.492 | 0.595 | -0.751 | 0.994 | -1.484 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| id_91 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |